Wood pellet processing plant
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Wood pellet plants combine the complete procedure of biomass particle production, including all processes from drying out to squashing, granulation, cooling, testing and packaging. Plant may be arranged or customised in a variety of ways according to need as well as the degree of automation in cooling, packaging, and feeding.
[edit] Process
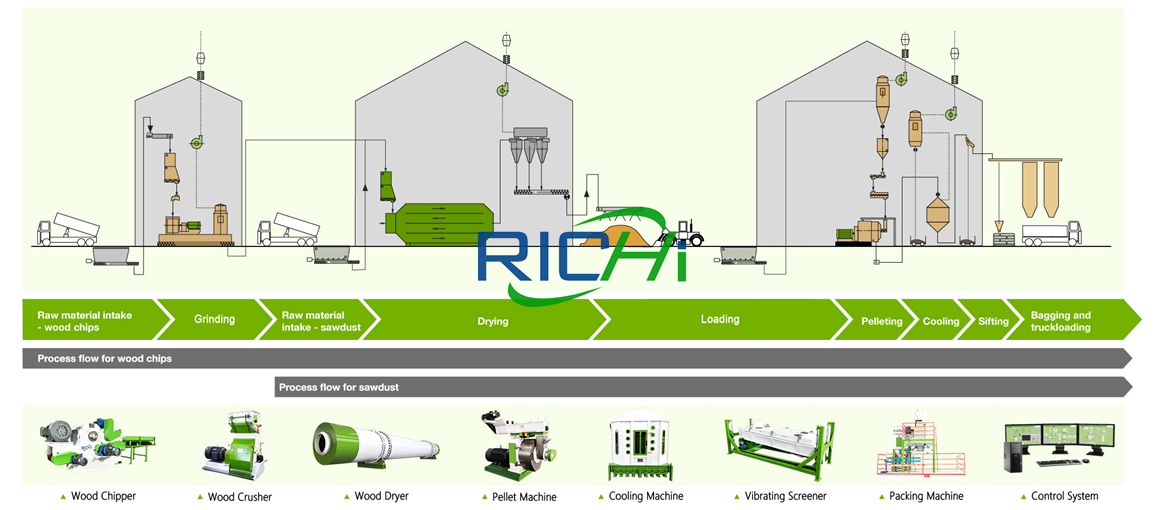
Appropriate raw materials are selected for natural fibres such as logs, branches, sawdust, rice husks, etc. These enter by conveyor belt and are sent to the wood hammer mill. On leaving in a crushed form these are directly send onward by the screw conveyor. This leads into the drum, similar to a clothes dryer, where materials are mixed with hot air. The dried material is accumulated by a cyclone separator, and then exits from the bottom of the airlock.
The next stage is the conditioner which is entered again via the screw conveyor, this conditions the material to the ideal level. Once achieving the intended moisture level the material is sent to the pelletising chamber, this performs a granulation process, with the material exiting as small round pellets of 2-12mm. The pellets then enter the cooler, drying the pellets to below 10%, and also cooling them to a regular temperature.
The remaining powder passes through the rotary category screener, which can separate out unqualified materials and granulate these once again. The screened pellets are loaded by an automated weighing device and then sealed by an automatic stitching device.
The complete set that makes up a wood pellet plant is not just timber pellet production equipment, it also a variety other treatment equipment according to the sort of resources and humidity.
If the raw materials arrives in larger sizes such as whole branches, it needs to be crushed into timber chips less than 5mm by a separate crusher, if it arrives smaller it can enter directly. If the humidity of the raw material is 15%-20%, it can enter the device directly, if it is higher than 20%, it has to be dried to 15-20% prior to granulation.
[edit] Renewable
As a renewable fuel, timber pellets have several advantages, such as high calorific worth, reduced emissions, huge particle proportion or compression after moulding, small volume, and combustion resistance. They have a higher level of processing than wood chips but due to their form can often be used more easily in small and large automated heaters, from industry to individual homes as an alternative fuel. Wood pellets can also utilise wood waste from saw mills and carpentry workshops.
Making use of wood pellets as a fuel is a realistic alternative environmental power resource that can help reduce carbon emissions, and has been used both in rural and urban locations.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.